A torque converter is a fluid coupling that allows the engine to spin somewhat independently of the transmission. While commonly used in automatics, enthusiasts explore its potential in manuals, seeking torque multiplication at low speeds without clutch engagement, offering a unique blend of performance and smooth operation.
What is a Torque Converter?
A torque converter is a fluid coupling device that connects the engine to the transmission, allowing smooth power transfer without mechanical interruption. It uses pressurized fluid to engage the impeller, turbine, and stator, enabling torque multiplication at low speeds. Commonly used in automatic transmissions, it replaces the clutch, providing seamless acceleration. Its design allows the engine to spin independently of the transmission, enhancing low-speed performance. While traditionally part of automatics, enthusiasts explore its integration into manual transmissions for improved torque delivery and smoother operation, blending the benefits of both systems in unique applications.
Historical Context of Torque Converters in Manual Transmissions
The concept of integrating torque converters into manual transmissions dates back to the early development of automatics in the 1920s. Porsche’s Sportomatic, introduced in 1968, combined a manual gearbox with a torque converter, offering a unique driving experience. This system aimed to provide smooth acceleration without manual clutch engagement. While not widely adopted, it showcased the potential of blending manual control with automatic convenience. Historical experiments like these laid the groundwork for modern explorations, such as Garage54’s unconventional modifications, demonstrating the enduring interest in hybridizing manual and automatic technologies for enhanced performance and usability.

The Role of Torque Converters in Manual Transmissions
Torque converters in manuals enhance low-speed acceleration by multiplying torque, allowing smooth vehicle movement without clutch engagement, similar to automatics, while retaining manual gear control.

How Torque Converters Differ from Traditional Clutches
Torque converters differ from traditional clutches by using fluid coupling to transfer power, eliminating the need for manual clutch engagement. Unlike clutches, which mechanically connect and disconnect the engine, torque converters provide smooth, continuous power transfer. They allow the engine to remain engaged even when the vehicle is stationary, offering low-speed torque multiplication without driver input. However, torque converters can introduce inefficiencies and heat generation, unlike clutches, which maintain direct mechanical control. This fundamental difference impacts both performance and driver experience, making torque converters more akin to automatic transmissions than manual systems.
Advantages of Using a Torque Converter with a Manual Transmission
Using a torque converter with a manual transmission offers smooth power delivery and low-speed torque multiplication, reducing the need for frequent clutch engagement. It allows the vehicle to move from a standstill without stalling, enhancing ease of use in stop-and-go traffic. Additionally, torque converters provide consistent power transfer, reducing wear on the clutch and transmission components. They also enable better control in challenging driving conditions, such as hills or heavy loads, by maintaining optimal engine torque. This setup combines the benefits of automatic smoothness with manual gear control, appealing to drivers seeking a blend of convenience and performance.
Disadvantages and Challenges of Combining Torque Converters with Manual Transmissions
Combining a torque converter with a manual transmission presents several challenges; The system adds complexity and cost, as it requires additional components like a brake mechanism to hold the converter during gear shifts. This increases the overall weight and reduces fuel efficiency. Torque converters can also introduce power loss due to slip, especially during aggressive acceleration. Additionally, driver engagement may decrease as the clutchless operation removes the tactile feedback of manual shifting. Engineering a seamless integration is difficult, often leading to compromises in performance, making it less practical for most drivers compared to traditional manual or automatic setups.
Practical Applications and Examples
Torque converters on manual transmissions have been explored in unique setups, such as Garage54’s experimental installation and historical systems like Porsche’s Sportomatic, blending manual control with automatic-like smoothness.
Case Study: Garage54’s Experiment with Torque Converters on Manual Transmissions
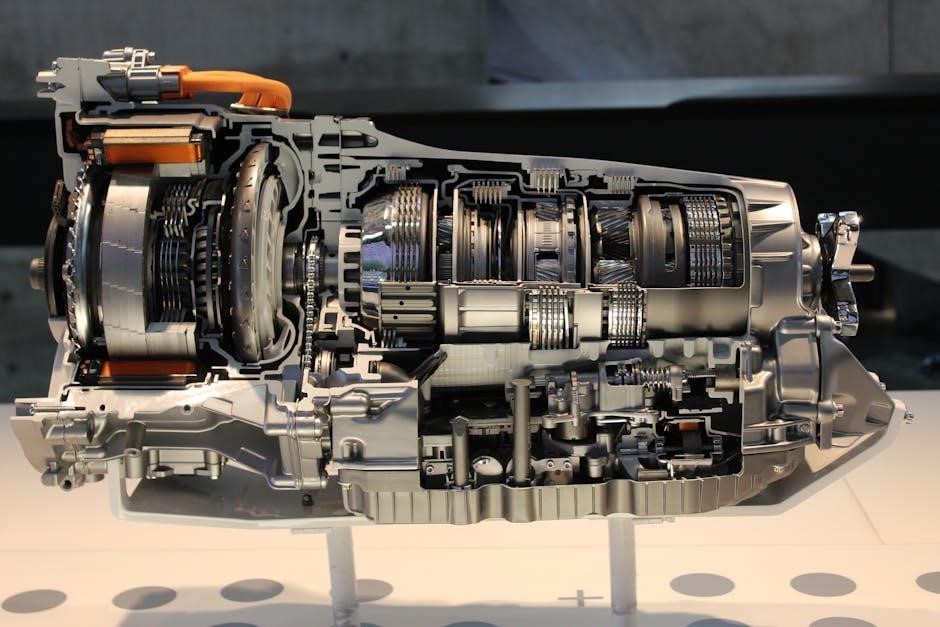
Garage54’s innovative experiment involved installing a torque converter on a manual transmission, showcasing its potential benefits and challenges. The setup allowed for smooth low-speed acceleration and torque multiplication, enabling the vehicle to creep forward without clutch engagement. However, the system required additional components, such as a brake mechanism, to facilitate gear changes. While the experiment demonstrated the feasibility of combining a torque converter with a manual transmission, it also highlighted complexities in maintaining driver control and synchronizing shifts. This project provides valuable insights into the practicality and limitations of such a hybrid drivetrain configuration.
Historical Precedents: Porsche’s Sportomatic Transmission
Porsche’s Sportomatic transmission, available from 1968 to 1980, combined a manual gearbox with a torque converter, offering a unique driving experience; This system allowed the car to creep forward without clutch engagement, providing smooth low-speed operation. It featured a torque converter that engaged gradually, eliminating the need for a manual clutch during takeoff. The Sportomatic was particularly popular in urban environments, where frequent stops and starts were common. Although it lacked the direct control of a traditional manual, it showcased the potential of integrating torque converters into manual transmissions, influencing future design concepts in automotive engineering.
Modern Applications in Performance and Specialty Vehicles
Modern performance and specialty vehicles occasionally experiment with torque converters in manual transmissions to enhance low-speed torque delivery and smoothness. This setup is particularly beneficial in extreme applications, such as heavy-duty towing or racing, where immediate torque multiplication is crucial. Some aftermarket solutions integrate torque converters with manual gearboxes, offering improved drivetrain efficiency and reduced wear on mechanical components. These systems are often custom-engineered to balance the benefits of torque multiplication with the driver engagement of a manual transmission, catering to niche markets where unique performance requirements are prioritized.

Performance and Driveability Considerations
Torque converters in manual transmissions can enhance low-speed acceleration and torque multiplication, improving drivability in specific scenarios like heavy-duty towing or racing, where instant power delivery is crucial.
Low-Speed Acceleration and Torque Multiplication
A torque converter significantly enhances low-speed acceleration by multiplying engine torque, allowing the vehicle to gain momentum more efficiently from a standstill. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios where rapid acceleration is needed, such as merging onto a busy highway or towing heavy loads. The fluid coupling within the torque converter ensures smooth power delivery, eliminating the abruptness often associated with manual clutches. As a result, drivers experience a more seamless and controlled takeoff, especially in low-speed conditions where traditional clutches may struggle to provide consistent torque transfer.
Impact on Fuel Efficiency and Power Delivery
The integration of a torque converter with a manual transmission can lead to a slight reduction in fuel efficiency due to the inherent slip in the fluid coupling, which generates heat and consumes power. However, this trade-off is often offset by improved power delivery at low speeds, where torque multiplication enhances acceleration. In city driving or heavy traffic, where frequent stops and starts are common, the torque converter’s ability to maintain smooth engagement can be advantageous, despite the minor efficiency loss compared to a traditional manual clutch system.

Driver Experience and Usability
The addition of a torque converter to a manual transmission creates a unique driving experience, offering smooth, clutch-free engagement at low speeds; This eliminates the need for constant clutch operation, making city driving and heavy traffic significantly easier. However, it introduces a learning curve for drivers accustomed to the direct feel of a manual clutch. The torque converter’s operation can feel less engaging for enthusiasts who enjoy the tactile connection of shifting gears. While it enhances usability in certain scenarios, it may not appeal to purists who value the traditional manual driving experience. Balancing convenience and control remains key to its practicality.

Technical and Installation Challenges
Adapting a torque converter to a manual transmission requires complex modifications, including custom engineering and integration with existing systems, posing significant technical and installation hurdles.
Modifications Required for Installation
Installing a torque converter on a manual transmission demands significant modifications. A custom adapter plate is needed to mate the converter to the transmission, alongside flywheel changes for proper engagement. Additional components like a brake system may be required to facilitate shifting. The drivetrain must be reinforced to handle increased torque, and electronic controls may need adjustment. These modifications are complex, often requiring bespoke engineering solutions, and can introduce challenges like drivetrain stress and increased cost. The process is not straightforward, making it a specialized endeavor for skilled enthusiasts or professionals.
Integration with Existing Transmission Systems
Integrating a torque converter with a manual transmission requires precise engineering to ensure compatibility. The converter must align with the transmission’s input shaft, necessitating custom adapters and potentially altering the bellhousing. Electronic controls may need recalibration to synchronize torque delivery with manual shifting. Hydraulic systems must also be adapted to manage the converter’s operation seamlessly. This integration is challenging due to the manual transmission’s mechanical nature, often leading to complex setups. Proper alignment and system harmony are crucial to avoid drivetrain issues and ensure smooth power transfer, making integration a delicate and specialized task.
Additional Components Needed for Operation
Installing a torque converter on a manual transmission requires additional components to ensure proper functionality. A hydraulic system, including a pump and fluid reservoir, is necessary to manage the converter’s fluid coupling. A dedicated cooling system may be needed to prevent overheating during operation. The drivetrain must also be reinforced, with components like the input shaft and bellhousing potentially requiring upgrades. An external brake system might be added to halt the converter during gear shifts. Electronic controls may be integrated to monitor and regulate torque delivery, ensuring smooth power transfer. These additions complicate the setup but are essential for reliable operation.
Potential for Future Development and Innovation
Torque converters in manual transmissions offer promising potential for future innovation, blending smooth power delivery with manual control, particularly in high-performance or specialized applications, as technology advances.
Future advancements could see torque converters optimized for manual transmissions, enhancing low-speed torque multiplication and seamless power delivery. Innovations in fluid dynamics and material science may improve efficiency and reduce weight. Integration with hybrid systems could offer eco-friendly solutions. Additionally, intelligent torque converters that adapt to driving conditions may emerge, providing a balance between performance and fuel efficiency. These developments could redefine the role of manual transmissions, making them more versatile and appealing to a broader range of drivers.
Final Thoughts on the Practicality of Torque Converters in Manual Transmissions
While torque converters offer smooth low-speed operation and torque multiplication, their integration with manual transmissions remains niche. The added complexity and potential inefficiencies at higher speeds make them less practical for most drivers. However, for specialized applications or extreme conditions, they provide unique benefits. Enthusiasts may appreciate the blend of automatic-like convenience and manual control, but widespread adoption seems unlikely due to cost and performance trade-offs compared to traditional manual or automatic systems.